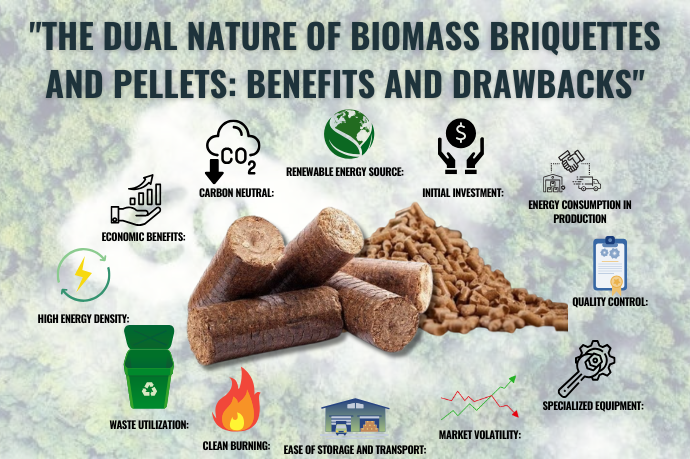
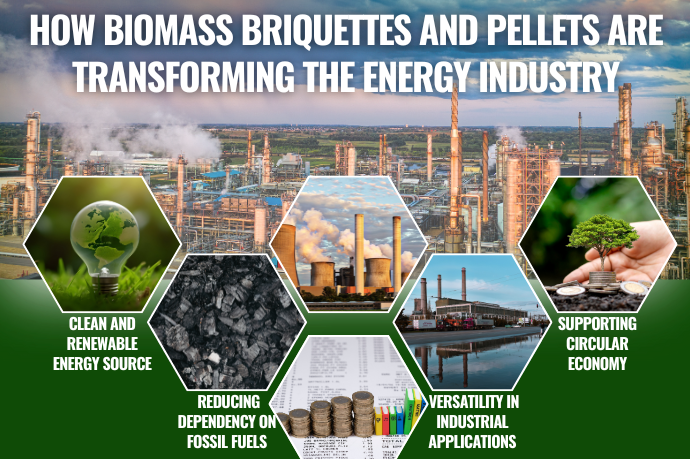
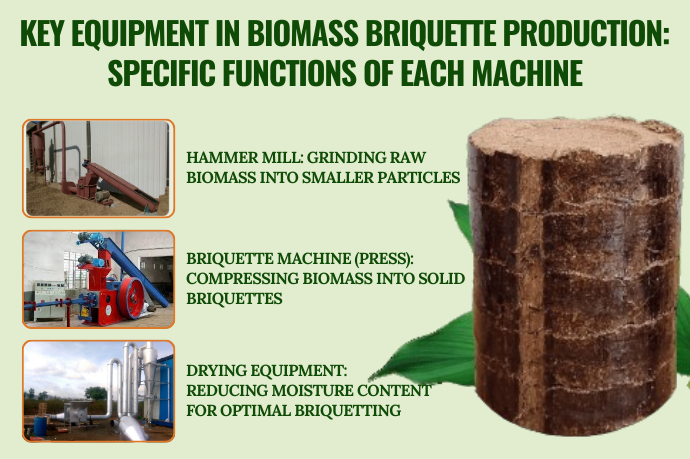
From Waste to Wealth – Transforming Organic Materials into Clean Energy
Biomass briquettes and pellets are gaining popularity as eco-friendly, renewable alternatives to traditional fuels like coal and wood. Made from organic waste materials such as sawdust, agricultural residues, and even food waste, these biofuels offer a cleaner, more sustainable energy solution. But how exactly are they made? Let’s take a quick look at the step-by-step process behind their production.
1. Collection of Raw Materials
The first step in creating biomass briquettes and pellets is gathering the raw materials. Biomass feedstocks—such as sawdust, wood chips, rice husks, wheat straw, and other agricultural by-products—are collected from local sources. These materials are typically waste from industries like woodworking, agriculture, and forestry. Instead of going to landfills, they are repurposed as valuable energy sources, making the process both sustainable and cost-effective.
2. Drying
Once collected, the biomass is dried to reduce its moisture content to around 8-12%. This is an essential step because excessive moisture can hinder the combustion process, leading to inefficient burning. Drying ensures that the biomass is in the optimal condition for the next stages of production and helps improve its energy output when burned.
3. Grinding
After drying, the biomass is ground into a fine powder or small particles. This step ensures uniformity and makes the material easier to compress. Grinding is crucial for creating consistent, high-quality pellets or briquettes that will burn efficiently and release the maximum amount of energy.
4. Compression into Briquettes or Pellets
Next, the finely ground biomass is fed into a briquette or pellet machine, where it’s compressed under high pressure. This compression process fuses the particles together without the need for chemical binders. The result is a solid fuel—either cylindrical pellets or block-shaped briquettes—that is denser and has a higher calorific value (more energy per unit volume) than the raw biomass material.
5. Cooling and Packaging
Once compressed, the briquettes or pellets are cooled to harden and stabilize. This cooling process ensures the final product holds its shape and is ready for storage and transport. After cooling, the biomass fuel is packaged and ready to be distributed to consumers or businesses for use in heating, cooking, or industrial applications.
Biomass briquettes and pellets are a prime example of how waste can be turned into a valuable resource. Through this process, organic by-products are converted into renewable energy that is cleaner and more efficient than traditional fossil fuels. These fuels not only help reduce waste but also lower carbon emissions, making them a key player in the transition toward a more sustainable energy future.
Ready to make the switch to cleaner energy? Biomass briquettes and pellets offer a sustainable solution for heating, power generation, and more.