Biomass briquettes and pellets are proving to be a highly useful and sustainable energy sources in various industries. These compact, solid fuels, made from agricultural waste, wood residues, and other organic materials, have gained significant traction in the energy sector due to their environmental, economic, and operational benefits.
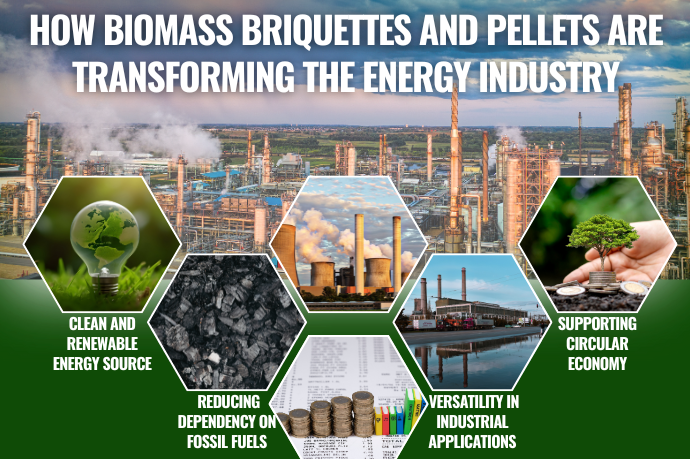
1. Clean and Renewable Energy Source
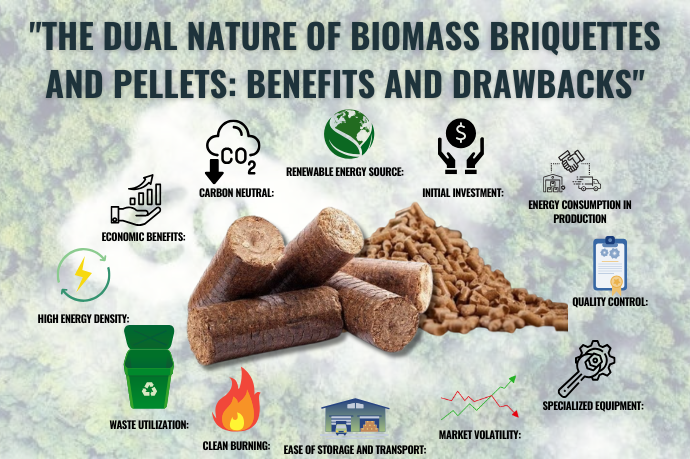
One of the most significant advantages of Biomass briquettes and pellets is that they are carbon-neutral. When burned, biomass releases carbon dioxide (CO2), but this is the same CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth, creating a balanced carbon cycle. Unlike fossil fuels, which release additional carbon that has been stored for millions of years, biomass helps to lower overall greenhouse gas emissions.
This makes biomass briquettes Biomass briquettes and pellets a crucial tool in the fight against climate change, offering the energy industry a cleaner alternative to coal and other fossil fuels.
2. Reducing Dependency on Fossil Fuels
Biomass briquettes and pellets provide a reliable and renewable source of energy that reduces dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels. As the world moves toward a more sustainable future, switching to biomass is a key step in minimizing the environmental impact of energy production. Biomass is locally sourced, reducing the need for expensive and environmentally harmful transportation of fossil fuels, and it supports energy security by fostering local energy production.
3. Lower Emissions and Pollution
Compared to traditional fossil fuels, Biomass briquettes and pellets burn cleaner, producing fewer emissions such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This makes them an attractive option for industries seeking to meet stricter environmental regulations. The lower levels of air pollution from burning biomass contribute to better air quality and overall public health.
4. Cost-Effective Solution
Biomass briquettes and pellets are often more affordable than fossil fuels, particularly in regions where agricultural residues and organic waste are abundant. The production of Biomass briquettes and pellets can help reduce waste, making them not only a more sustainable energy source but also a cost-effective one. In the long term, adopting Biomass briquettes and pellets can help industries save on fuel costs while contributing to a cleaner environment.
5. Versatility in Industrial Applications
Biomass briquettes and pellets are used across a wide range of industrial sectors, including manufacturing, power generation, and heating. They can be burned in furnaces, boilers, and power plants for electricity generation or industrial heating processes. Biomass briquettes and pellets are especially useful in areas where other renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, may not be as reliable or available.
For example, biomass can be co-fired with coal in existing power plants, reducing carbon emissions while allowing these plants to continue operating without the need for extensive infrastructure changes. Biomass also serves as a viable option for district heating systems, which provide energy to large residential and industrial areas.
6. Supporting Circular Economy
The production of Biomass briquettes and pellets promotes a circular economy by transforming agricultural waste and other organic materials into a valuable energy resource. Instead of sending waste to landfills, Biomass briquettes and pellets repurpose these materials, contributing to waste reduction and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Biomass briquettes and pellets play an essential role in the energy industry by providing a renewable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly energy source. With their ability to reduce carbon emissions, support energy security, and replace fossil fuels, Biomass briquettes and pellets are poised to be a cornerstone of the future energy landscape. As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, Biomass briquettes and pellets will become an increasingly important tool in achieving cleaner, greener energy production.